Belt Technologies has developed an innovative concept in flat belt tracking called the ISP (Independently Steerable Pulley) which can be used in the following system designs:
- Two pulley conveyor systems, where the ISP is the idler or driven pulley
- Systems with multiple idler pulleys on a common shaft
- Systems with serpentine or other complex belt paths
Steering flat belts with an ISP is based on the concept of changing tension relationships across the width of the belt by adjusting the angle of the pulley relative to the belt.
Rather than moving the pulley shaft left/right or up/down by pillow block adjustment, the ISP fits a variable steering collar and sealed bearing assembly to the body of the pulley.
ISP Components:
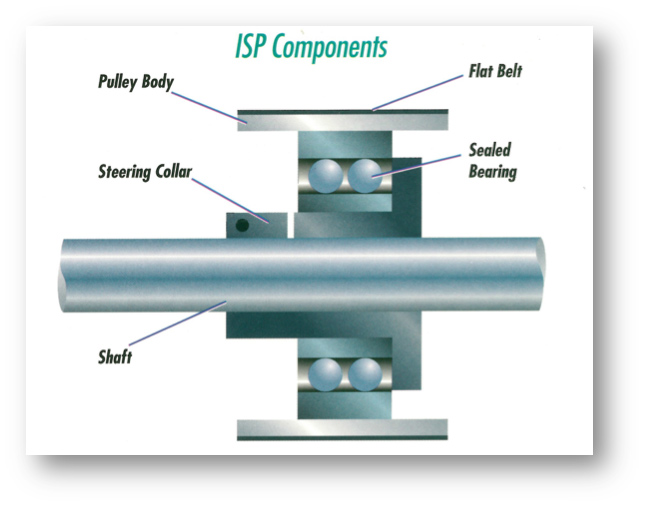
The steering collar is designed with either a skewed or an offset bore. When rotated, the collar changes the angle of the pulley body, resulting in controlled bi-directional movement of the belt across the pulley face.
The ISP is exclusively available from Belt Technologies. It provides a simple method of steering flat metal belts. Users may combine ISP steering with the traditional belt tracking designs of crowning, flanging, and timing elements, to create a synergistic belt tracking system which efficiently and precisely steers the belt to specified tracking parameters.
Unique Characteristics and Advantages of the ISP
- Flat belts are tracked quickly by rotating the steering collar.
- ISP designs minimize down time when replacing belts on production machinery.
- ISP system is easy to use and requires no special tools or training.
- ISP simplifies the design and assembly of conveyor systems using flat belts.
- Existing idler pulleys can normally be retrofitted to an ISP without major system modifications.
- No maintenance is required once the belt tracking parameters have been established.
- It prolongs belt life by minimizing side loading when using flanges and timing pulleys.
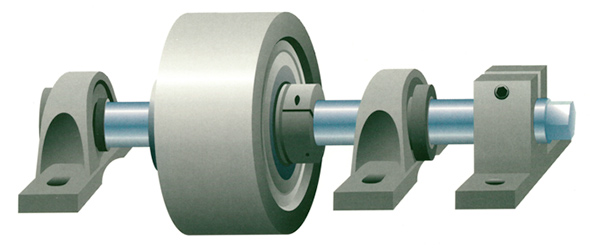
ISP Pulley (picture and cross section view)

Installation and Use
The ISP is mounted to the system frame using commercially available pillow blocks. A clamp is used to prevent the shaft from turning.
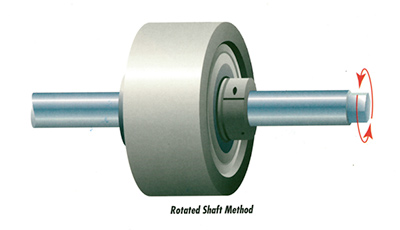
The Rotated Shaft Method of ISP Flat Belt Tracking
- Used with systems having a single pulley on the shaft.
- Is ALWAYS used when the pulley body is a Capped Tube design.
- Is NEVER used when multiple pulleys are on a common shaft.
- Used selectively when the ISP is a steering roll in a multiple pulley system.
Secure the ISP to the shaft using the split collar and locking screw built into the ISP. Rotate the shaft and collar as a unit. When the desired tracking characteristic is obtained, prevent the shaft from rotating by securing the shaft clamp. The pulley body now rotates about the bearing built into the ISP assembly. This method allows the belt to be tracked while running under tension.
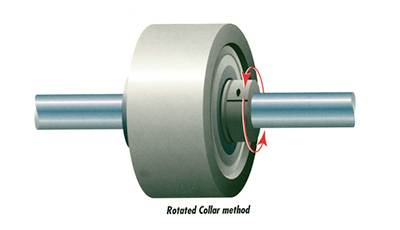
The Rotated Collar Method of ISP Flat Belt Tracking
- Use to individually adjust each belt/pulley combination when there are multiple pulleys on a common shaft.
- Use when systems have a cantilevered shafting typical of serpentine and other complex belt path systems. It is recommended these adjustments be made only when the belt is at rest.
Fix the shaft via the shaft clamp, loosen the locking screw of the steering collar and rotate the steering collar about the shaft. When the desired belt tracking characteristic is obtained, secure the locking screw.
Which Design Is Right For You?
Applications for this new product are far reaching, so Belt Technologies individually designs and manufactures Independently Steerable Pulleys to suit your needs. Contact Belt Technologies to discuss your questions or for design assistance.
Belt Technologies is the worldwide leader in the design and manufacturer of application specific pulleys, metal belts and drive tapes. Our products provide unique benefits for machinery used in precision positioning, timing, conveying, and automated manufacturing applications.
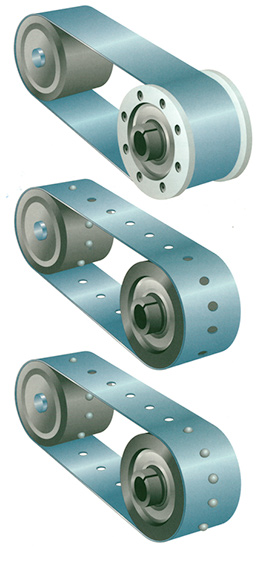
System Configuration
Number 1 – The drive pulley is a friction drive pulley
- The ISP is a friction driven pulley. This configuration is specified for tracking accuracy of 0.030″ (0.762mm) or greater.
- Teflon® flanges are attached to the pulley body to establish a lateral constraint. The steering feature of the ISP is used to set one edge of the belt against the flange with minimum side loading to the belt.
System Configuration
Number 2 – The drive pulley is a timing pulley
- The ISP is a friction driven pulley. The teeth of the drive pulley and the perforations of the belt establish a lateral constraint, with the steering feature of the ISP used to minimize side loading of the belt perforations. Tracking accuracy is between 0.008″ (0.203mm) and 0.015″ ( 0.381mm) for metal belt systems.
OR
- The ISP is a timing pulley. The teeth of the ISP and the perforations of the belt are used for precise tracking control of the belt, with the steering feature of the ISP used to minimize side loading of belt perforations. Again, tracking accuracy is 0.008″ (0.203mm) to 0.015″ ( 0.381mm) for metal bells.
Note: Although it is generally not recommended to have timing elements in both the drive and driven pulleys, this design can be used selectively on metal belt systems with long center distances between pulleys and in applications where particulate accumulation on the surface of the pulley continuously changes the tracking characteristic of the belt.

Belt Technologies – Independently Steerable Pulleys
We’re pleased to offer you the opportunity to download Belt Technologies – Independently Steerable Pulleys in PDF format. (Adobe Acrobat Reader is required, high speed internet connection recommended).


